VOLUME 216: WEEK ENDING SEPTEMBER 14, 2024
Higher shelter and transport services costs drove the stronger-than-expected rise in core inflation in August. Despite this, the disappointing inflation data makes it more likely that officials will be cautious about easing, starting with a 25 basis point rate cut.
Although core inflation edged up slightly to 3.3% from 3.2%, headline inflation decreased to 2.6% from 2.9%, marking its lowest point since March 2021. This decline is partly attributed to falling global oil prices, which have been pulling down gasoline costs. The downward trend is expected to continue in September, bringing headline inflation closer to 2%.
While August saw a stronger rise in core inflation, it has averaged close to 2% annualized over the past three months. As a result, Fed officials are likely to focus more on labor market conditions in their next FOMC meeting.
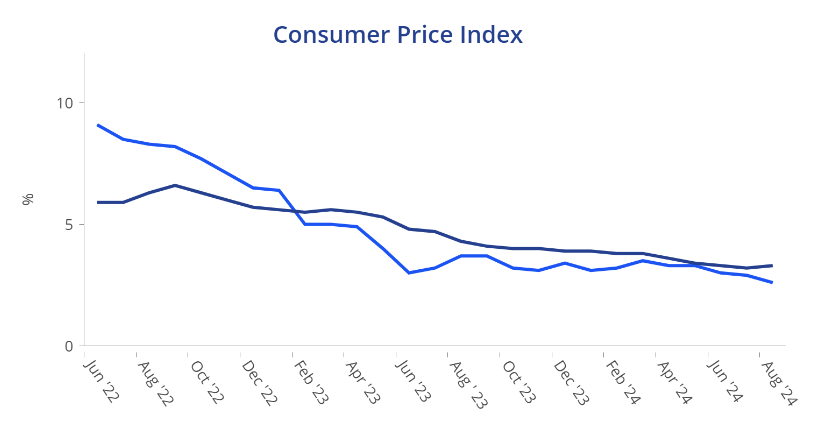
Source: Oxford Economics, Trading Economics